HETEROGENOUS CATALYSTS
Availability of a partially filled 3d subshell which allows for the ready exchange of electrons to and from reactant molecules, thus facilitating the formation of weak bonds with the reactant molecules
HOMOGENOUS CATALYSTS:
Ability to exist in different oxidation states, and relative ease with which they can be converted from one oxidation state to another
Warning: this is not a substitute for practice papers. This blog focuses on H2 A level Bio and Chem (syllabus 9647 and 9648) Use with discretion.
Showing posts with label subject:chem. Show all posts
Showing posts with label subject:chem. Show all posts
Thursday, October 16, 2014
Tuesday, July 15, 2014
Warning signs for a pseudo-first order reaction
- Excess of reactant - since concentration of reactant does not change significantly, so can treat as a first-order reaction
- Solvent is a reactant
- Use of catalyst
Tuesday, June 3, 2014
Describe the structure of a beta-pleated sheet of a spider silk protein.
Hydrogen bonds form between the C=O group of a peptide in one strand and the N-H group of another peptide in the adjacent strand. R-groups project above and below the beta-pleated sheet.
Outline the procedure of a titration experiment to determine the concentration of ammonia in the organic layer.
NB: Given 0.010 mol dm-3 hydrochloric acid, methyl orange indicator and lab apparatus commonly used for titration.
- Fill up a burette with 50.00cm3 of 0.010mol/dm3 HCl
- Using a dry pipette, transfer 10.0 cm3 of the organic layer into a 250cm3 conical flask.
- Using a measuring cylinder, add 20 cm3 of deionised water into the conical flask, then add 2-3 drops of methyl orange.
- Titrate the resulting mixture against 0.010mol/dm3 HCl until the colour of methyl orange changes from yellow to orange.
- Repeat the titration until 2 consistent readings are obtained.
Saturday, May 31, 2014
Equilibrium constant
Equilibrium constant of salt MX:
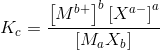
For homogenous equation A + B --> C + D (i.e. all in the same state):
Formatted in LaTeX using the CodeCogs editor.
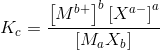
For homogenous equation A + B --> C + D (i.e. all in the same state):
Formatted in LaTeX using the CodeCogs editor.
What do you understand by the term 'Dynamic equilibrium'?
Dynamic equilibrium refers to a reversible reaction in which the rate of the forward reaction equals the rate of the backward reaction and there is no net change in the concentration of ions.
Thursday, May 22, 2014
Standard electrode potential
The standard electrode potential, E⦵, of a half-cell is the electromotive force measured at 298 K between the half-cell and the standard hydrogen electrode, in which concentration of any reacting species is 1M/gaseous species is at 1 atm.
Remember to indicate the surrounding temperature when drawing half-cells!
The standard cell potential, E⦵cell is the maximum potential difference between two half-cells under standard conditions.
The standard cell potential, E⦵cell is the maximum potential difference between two half-cells under standard conditions.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)
.gif)